Papillomas on the neck are one of the manifestations of an infectious disease caused by the human papillomavirus.These are benign skin formations.
Causes of papillomas on the neck
There is an etiological reason why papillomas start to grow on the neck or any other area of the human body - infection with the human papillomavirus (papillomavirus, HPV), which represents the papovaviridae family.There are more than 100 serotypes of this pathogenic agent, each of which has a different clinical picture of the disease (papillomas, condensomas, warts - these concepts are synonymous, different names are associated with the features of localization in a certain area).
The main routes of transmission are through domestic and sexual contact (conditioners of the perianal area).The virus can penetrate the skin only in the presence of mycorum or open wounds;In other cases, it cannot penetrate the protective barrier of the skin.
Information about the pathogen
- A high prevalence regardless of gender (however, it occurs more in women than in men), age or region) (according to some reports, 2/3 of the planet is infected with this virus).
- It contains double-stranded, circular, twisted DNA that can integrate into the human genome.
- Infection with some strains is associated with a high carcinogenic risk, especially in the case of permanent injury.Papillomas on the neck are caused by non-oncogenic strains of the virus.
- During the division process, the virus goes through two main stages.In the first stage, it is episomal (free), and at the same time, the main division of viral particles is formed.This phase is reversible (long-term remission occurs after treatment).In the second - integration - stage, the virus is inserted into the cell genome (the first step for cell degeneration and the formation of a malignant neoplasm).The first stage is transient and passes relatively quickly, the second is hidden and explains the presence of carriers.
- The basal layer of the epidermis is affected where the virus replicates.In the remaining layers, the pathogen can persist, but does not divide.If the virus is in the germinal layer, as it grows, the normal differentiation of all layers of this area is disturbed, the disturbances are especially strong at the level of the sponous layer.
- It is prone to long-term asymptomatic carriage in the body (from several months to one).It is rarely possible to determine the exact moment of infection - it is not at the first vague signs that begin during the period of intense clinical manifestations of treatment.
- To prevent infection, bivalent and quadrivalent vaccines are used, which are particularly effective against the 2 and 18 most oncogenic strains.
Predispose factors
- Non-compliance with hygiene rules.Since the virus is capable of living in the external environment for a long time, it is necessary to carefully follow the rules of personal hygiene when visiting public places (swimming pool, sauna, gym).
- Traumatic injuries to the skin.Microcracks or scratches on the skin (for example, the reason for rubbing the neck with a shirt collar) are enough for the virus to penetrate.
- Immune system dysfunction.Immunodisease of any origin creates favorable conditions for the development of any infection.For example, frequent colds and infectious diseases cause weakened immunity and the appearance of papillomas on the skin.
- Self-infection by scratching the skin.
- Systemic lifestyle disorders (stress, lack of physical activity, unhealthy diet).These factors affect the activity of all metabolic processes in the body and cause a decrease in the barrier function of the skin.
- Environmental factors affecting the reduction of the body's defenses (hypothermia, excessive ultraviolet exposure).
External manifestations of the disease
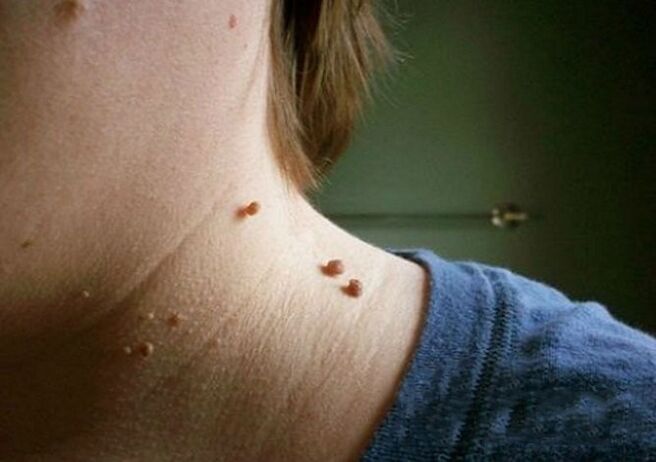
Cervical papillomas in the picture look like this:
- The growth is most often located on a wide base and is well above the surface of the skin.Less often, the base of the papilloma is represented by a thin thread (in this case, it occupies the position of the formation).The second option has a higher risk of injury.
- The boundaries of education are smooth and clear.
- The color does not differ from the surrounding skin.In rare cases, the adjacent tissue may be slightly paler or darker.
- The surface is often flat and smooth.Sometimes growths are possible at the head of the papilloma, whose surface is ribbed.
- The diameter varies widely - from 1-3 mm to several centimeters (small diameter papillomas are more common).
- Any place on the neck (back, side, front).Sometimes a face is involved.
As a rule, there are many lesions in the skin layers.
In very rare cases, papillomas on the neck can be malignant, that is, they degenerate into a skin tumor.This can occur as a result of infection with an oncogenic strain of HPV.
Signs that may indicate degenerative degeneration include:
- color change and heterogeneity (polymorphism);
- Change in boundary (confusion, loss of clarity);
- The appearance of asymmetry (it is impossible to get two equal halves when drawing a line with the conventional middle of a line);
- intensive growth;
- bleeding or ulceration (it is a non-specific sign, because it is also typical for a neoplasm for simple trauma);
- itching, burning, peeling;
- Screens are formed (the formation of a small girl around the central one).
The appearance of such symptoms does not necessarily mean the degeneration of the papilloma, but it means consulting a doctor and making a differential diagnosis, finding out whether it is a regular inflammatory mole or skin cancer.
How to get rid of papillomas on the neck
Treatment of papillomas on the neck is carried out only with a thorough pathological focus on the skin and an effect on the pathogen in the blood.
You can fight in several ways:
| Method |
Description |
| Medicinal methods |
The use of cytostatics and immunomodulators is aimed at suppressing the replication of the viral agent in the affected area and reducing its concentration in the blood.Some drugs (keratolytics) are applied directly to destroy the skin growth (they cause tissue necrosis). |
| Physical methods |
Cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation.The goal is to get rid of papillomas on the neck and other parts of the body.These methods can restore the aesthetic appearance of open areas and remove the viral reservoir - the skin tumor, but do not completely remove the virus from the body. |
| Combination therapy |
It combines the two previous options and is therefore the most effective. |
Treating papillomas with home remedies (for example, Celdandine juice) is ineffective and often dangerous;In any case, a necessary situation is consultation with a doctor.
Methods of physical destruction
It is possible to effectively reduce formations using the following physical methods:
| Method |
Description |
| Local exposure to concentrated acid solutions |
1.5% solution of zinc chloropropionate with 50% 2-chloropropionic acid, nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acids and copper nitrate trihydrate, etc.The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis by a specialist (dermatovenereologist, cosmetologist) according to surgical rules.The product is indicated with a spatula until it changes to the color of the resulting color (as soon as this happens, additional application should be stopped immediately).To completely cure papilloma, you need an average of 1-2 treatments. |
| Electrocoagulation |
Using a special electric knife, a targeted aculation of the joints is performed without affecting the underlying tissues (minimal effect on healthy skin cells).The method is most convenient when the formation has a long stem and small size. |
| Cryodestruction |
The lesion is exposed to liquid nitrogen;Ultra-low temperature causes tissue necrosis.In this way, it is good to remove connections with a wide base.The duration of nitrogen movement is selected by a specialist (1-5 minutes).After storage, a burn occurs that heals in an average of 10 days. |
| Laser removal |
The most modern and most delicate approach that allows you to remove formations in prominent places such as the neck.It has the most positive reviews.Using a light guide, the lesion is continuously exposed for 5 seconds to 3 minutes.The healing time is shorter than other methods (5-7 days).The technique is associated with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues due to the high accuracy of the effect. |
| Classic surgical removal (excision with a scalpel) |
Very rarely used, only for large lesions or suspected misfortune.The reason is that the lesions are often numerous, scattered on the neck and too small for excision;In addition, it may be possible to create a cosmetic defect on their own after surgical excision. |


















